The Role of Solar Energy in Reducing Chemical Industry’s Carbon Footprint
The Role of Solar Energy in Reducing Chemical Industry’s Carbon Footprint
Introduction
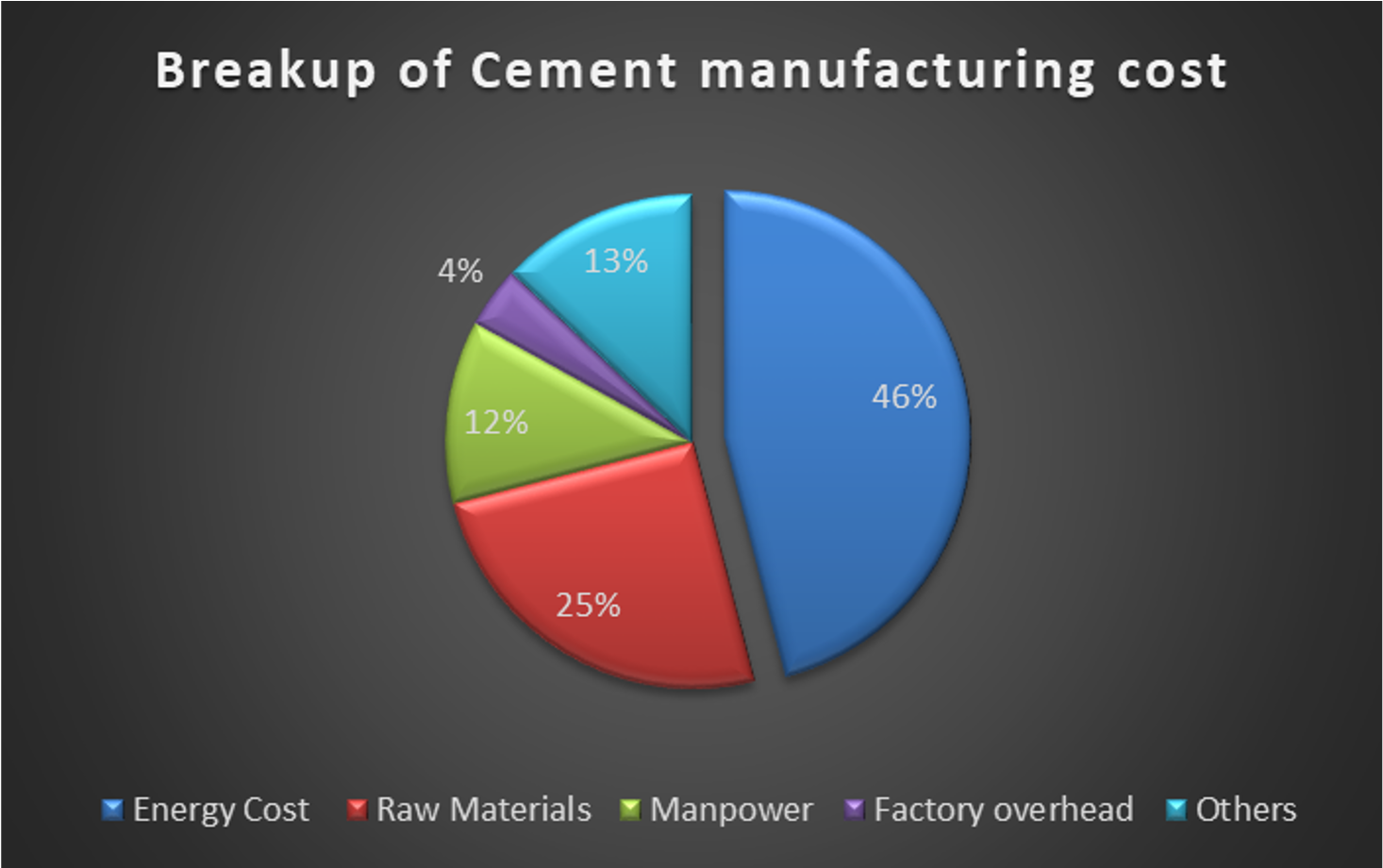
In the landscape of Indian industries, the chemical sector stands as a beacon of rapid growth and innovation. The Indian chemical industry is a major player in the global market. As of 2022, India is the world’s sixth largest producer of chemicals and the third largest in Asia. It contributes 7% of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). However, this progress comes with its own set of challenges, particularly in terms of environmental impact. The chemical industry is often referred to as a “hard to abate” sector due to its energy-intensive manufacturing processes, which include the production of basic chemicals, complex petrochemicals, and fertilizers. These processes inherently rely on high-temperature reactions and extensive heating and cooling cycles, making the industry a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions.
The role of solar energy in mitigating the environmental impact of this sector is becoming increasingly crucial. With India’s chemical industry being a significant contributor to the country’s emissions (6-8%), the urgency to reduce this footprint is paramount.Transitioning to solar energy offers a pathway to reducing these emissions and replacing fossil fuels with solar power, the chemical industry can significantly lower its carbon footprint.
What Does Carbon Footprint account for in the Chemical Industry?
According to global emissions data, the chemical industry worldwide accounts for a substantial share of total emissions, with figures reaching 6.0%. Globally, the chemical sector is the largest industrial energy consumer and the third largest industry sub sector in terms of direct CO2 emissions. According to global emissions data, direct CO2emissions from primary chemical production remained relatively constant at around 935 million metric tons in 2022.
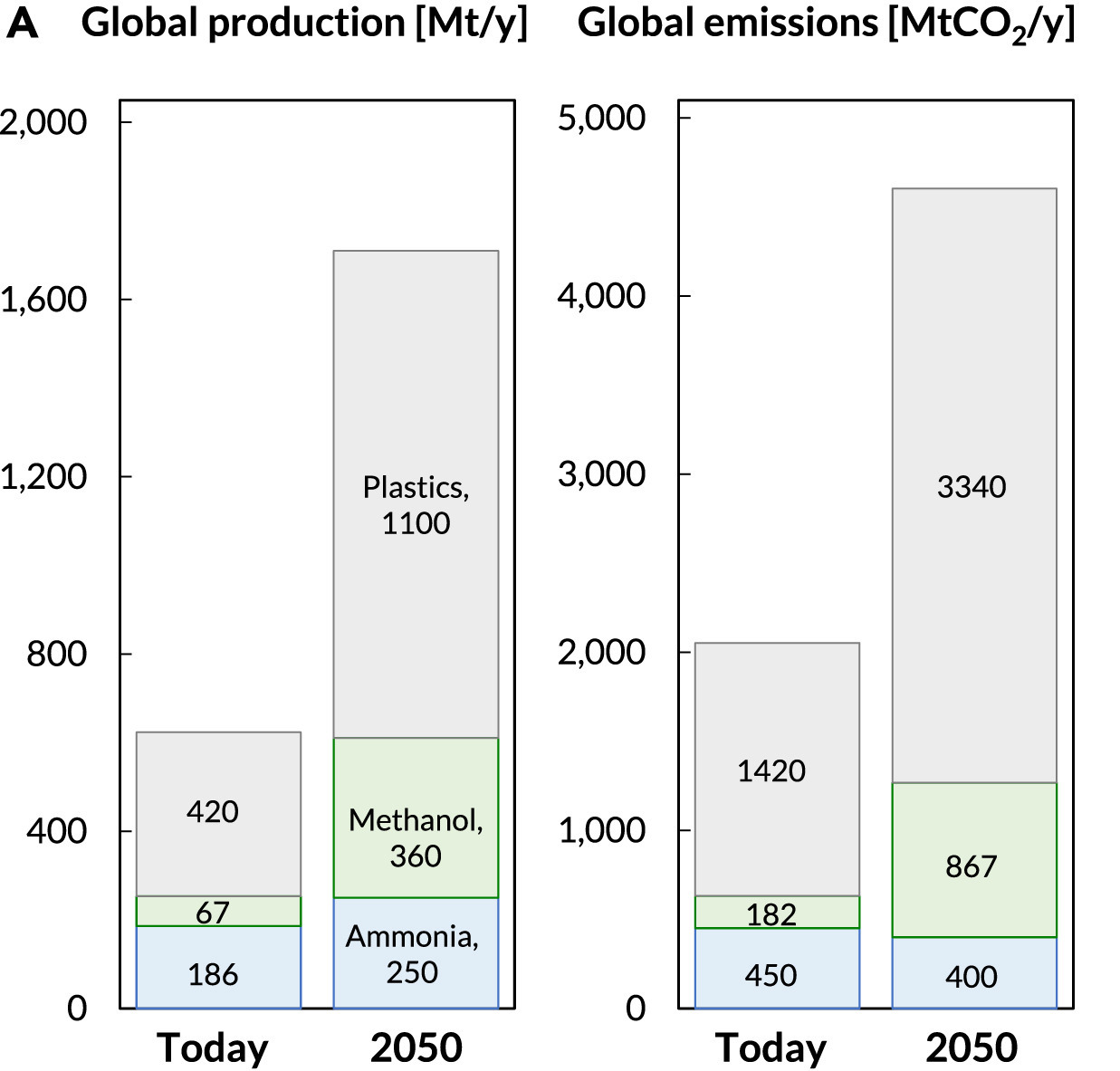
The chemical industry is a powerhouse of diverse processes, ranging from the production of basic chemicals to complex petrochemicals and fertilizers. These processes are inherently energy-intensive, often relying on high-temperature reactions and extensive heating and cooling cycles. This heavy reliance on energy, especially from fossil fuels, contributes significantly to the industry’s carbon footprint – the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an industry.
The Basics: Solar Energy and Carbon Footprint of the Chemical Industry
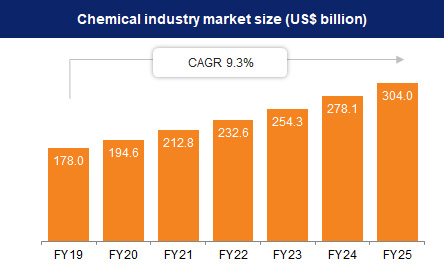
The Indian chemical industry is expected to grow at a rate of 11–12% during 2021–27. It is projected to reach a value of $290-310 billion by 2027. Combining all the stated facts, the chemical industry has and will continue to have a major share in India’s national GHG emissions. Much of these emissions are due to energy consumption, with coal being the primary energy source. Transitioning to solar energy offers a pathway to reducing these emissions. By replacing fossil fuels with solar power, the chemical industry can significantly lower its carbon footprint.
Electrification of Processes in the Chemical Industry (Scope 1 Emissions)
Electrification of industrial processes can effectively reduce Scope 1 emissions, which are direct emissions from owned or controlled sources. Processes like heating, cooling, and catalytic reactions, when powered by solar energy or any other source of green energy, not only reduce emissions but also enhance efficiency. This shift is pivotal for the chemical industry’s sustainability goals.
Use Solar to Cut Down on Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 2 Emissions)
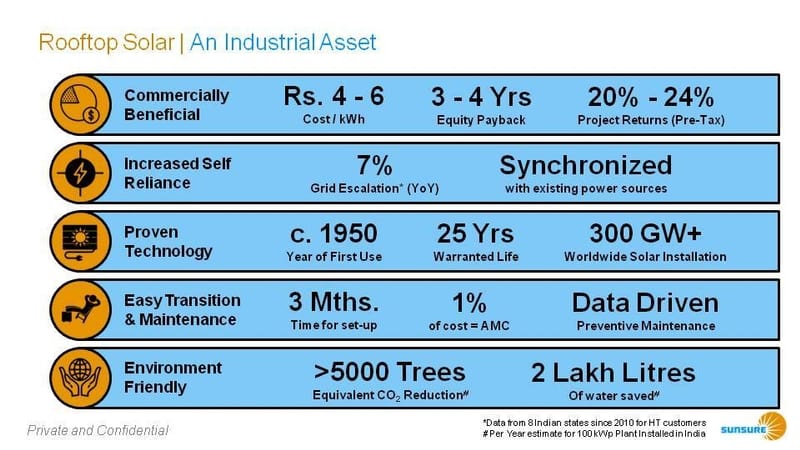
Solar solutions such as rooftop solar installations, ground-mounted solar farms, and Open Access solar power can significantly reduce Scope 2 emissions, which are indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy. These solar options offer the chemical industry a chance to source cleaner energy, thus reducing their dependence on the grid and fossil fuels.
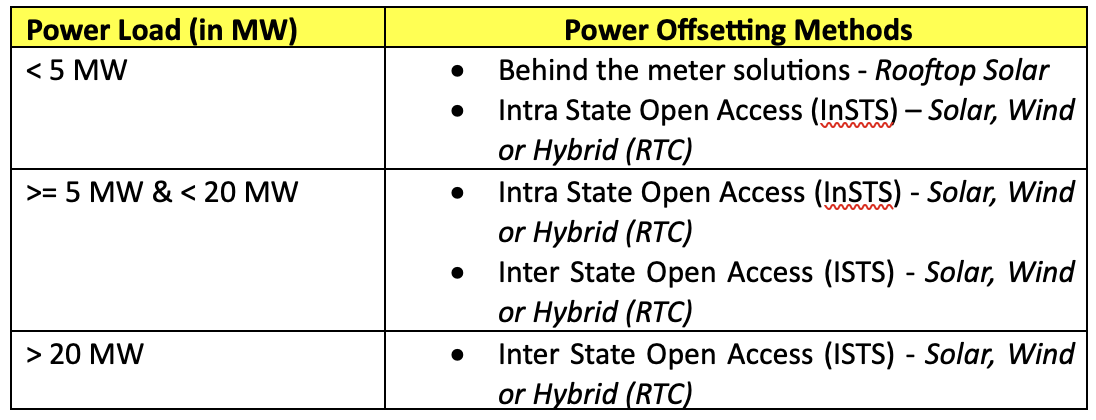
How Solar Energy Reduces Our Carbon Emissions in the Chemical Industry
Switching to solar energy not only has environmental benefits but also offers economic incentives. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels and utilizing solar power, chemical industries can see a reduction in power costs by 20-40%. This transition is a crucial step in achieving a lower carbon footprint and a more sustainable operation model.
Conclusion
Solar energy can help the chemical industries in India reduce their emissions and operational costs significantly. By transitioning to solar power, chemical industries can save upto 20-40% on their power costs per unit in INR, contributing to a lower carbon footprint and a more sustainable operation model.
Sunsure’s role in this transition is pivotal. By offering a range of solar energy solutions, from rooftop solar systems to large-scale solar farms and facilitating access to green power through various Intra-state and Inter-state power agreements (Solar, Wind andHybrid (RTC), Sunsure is well-positioned to assist the chemical industry in its journey towards reduced carbon emissions and financial savings. Moreover, Sunsure can support industries in achieving Net Zero emissions by providing Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) to offset their emissions.
FAQs
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint with Solar Power
- Solar power reduces carbon footprints by supplanting fossil fuels in electricity generation. Utilizing solar panels significantly lowers GHG emissions for both individuals and industries.
What Energy Sources Reduce Carbon Footprint?
- Renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power effectively reduce carbon footprints. These sources produce electricity without the GHG emissions associated with fossil fuels.
How Can Solar Energy Help Reduce the Scope 1 and Scope 2 Emissions?
- Solar energy reduces Scope 1 emissions by directly powering industrial processes with clean energy. For Scope 2 emissions, it provides an alternative to grid electricity, typically generated from fossil fuels, thereby reducing indirect emissions.

Shantanu Faugaat
Co-Founder, Director & COO at Sunsure Energy
Knowledge Hub
Related insights from the industry